
BILJOU
Forest water balance model
 - Silva Joint Research Unit
- Silva Joint Research Unit
Meteorology
Defining the meteorological variables
Climate variables that influence water balance are routinely measured on national synoptic networks such as
Météo-France and by other comprehensive networks (INRA, RENECOFOR and the six French public Water Agencies).
The variables required to run the Biljou© online modelling tool are the following
(see details
for instructions for using the online tool) :
- Solid and liquid precipitation (rainfall), in mm (1 mm = 1 Lm-2). The public online database Climathèque by Météo-France defines this variable as corresponding to "1-Hauteur de précipitations ». It is coded "pluie" or rain in the Biljou© meteo file.
- Global radiation corresponding to the entire solar spectrum as well as to radiation
from clouds, aerosols, etc. When considered over a 24 hour period, cumulative radiation is an energy that is
expressed in J.cm-2 (i.e. the unit conventionally used by Météo-France and the weather data file required by Biljou©).
Attention: it is important to note that in some databases, global radiation is expressed in MJ.m-2 (SI units).
The maximum level of global radiation, which is reached at the end of June, is about 3000 J.cm-2 (= 30 MJ.m-2). Vegetation absorbs only a fraction of global radiation: one part is reflected back into the atmosphere [more infoThe balance between all radiation fluxes over a canopy or over bare soil, incident and reflected, is called net radiation and can exist. ].
Météo-France (Climathèque) refers to this variable as "28-Rayonnement global”. It is coded "rgl" in the Biljou© weather file. - The mean air temperature. On a given day, the average air temperature (in Celsius) may be derived from hourly or
half-hourly measurements, or may be the average between the minimum (TN) and maximum (TX) temperatures throughout the day.
TN and TX measurements are more frequently used than hourly measurements. The value (TN + TX) / 2 has therefore been defined for
convenience as the reference value and is also a reliable estimator of average daily temperatures.
TN and TX data may also be useful to calculate the number of days of frost or heat.
Météo-France (Climathèque) refers to these two variables as "19-Température minimale sous abri" (19-Minimum temperature measured in shelters) and "21-Température maximale sous abri" (21-Maximum temperature measured in shelters).
The Biljou© meteo file codes this variable as "tsec". - Wind speed. Expressed in ms -1, wind speed can be measured at 2 meters in height (based on standard INRA
weather stations data) or at 10 meters in height (based on standard Météo-France data) above ground.
Météo-France (Climathèque) refers to this variable as “6-Moyenne des vitesses du vent à 10 mètres" (6-Average wind speed at 10 meters).
The Biljou© meteo file codes this variable as "vent".
In order for wind speed to be integrated in the Biljou© meteo file, it must be measured at a height of 2 meters. If the measurements are not performed at a height of 2 meters, the measured height Z (m) will need to be corrected by using the following conversion:Example: if V10M = 2 m.s-1 then V2m = 1.5 m.s-1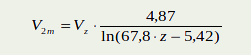
- Air humidity can be expressed by the relative humidity (“hum”, expressed in %, corresponding to the variable
named "33-Humidité relative moyenne" (33-Average relative humidity) by Météo-France (Climathèque)), or by the
vapour pressure deficit (“tvap”, expressed in hPa, corresponding to the variable named "41-Tension de vapeur moyenne"
(41-Average vapor pressure) by Climathèque, Météo-France). Only one of these two variables is required by the Biljou© meteo file.
Selecting one or the other depends purely on availability; in general, relative humidity is more commonly available.
Unlike mean air temperature, it is not recommended to calculate the mean relative humidity from daily minimum and maximum values.
Biljou© software calculates, for a given temperature, the saturated vapour pressure as being the maximum amount of vapour that can contain a given volume of air. The difference between this value and the measured vapour pressure (or the measurement recalculated from relative humidity) is called vapour pressure deficit (“dsat”, expressed in hPa). - Vapour pressure deficit (Dsat) is defined as the difference between partial water vapour pressure at saturation, at the given ambient temperature, and that which actually exists. It is expressed in Pa, kPa or hPa [more infoBefore meteorologists adapted the International System of Units, vapor pressure deficit was expressed in mb (=1 hPa) as was also used for atmospheric pressure. Both variables are now officially expressed in Pa, kPa or hPa].
Defining potential evapotranspiration (PET)
Agronomists have developed the concept called potential evapotranspiration or PET (expressed in mm.day-1), which is a climate index used to quantify the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available or the evaporative demand. PET is used in water balance models to calculate the actual evapotranspiration or AET (see the page Water balance).
A variety of formulas exist for calculating PET, each offering a different approach:
- The Penman formula provides a realistic representation of the evapotranspiration process since it corresponds to a comprehensive energy balance calculation using radiative and convective terms. For a closed canopy (LAI > 6 m2 m- 2) with unlimited water, the ETR / ETP ratio is about 0.75.
- The Penman–Monteith formula, considered a standard by agronomists, is a refined version of the Penman formula. It takes into account resistance factors in water transfer (crop height, stomatal resistances, canopy roughness, etc.). However, the required parameters are not often readily available for forest canopies and this formula does not provide any significant improvement in PET calculation. For calculating forests PET, the Penman and Penman-Monteith formulas are perfectly correlated (r2>0,99) with a bias of roughly 1%.
- The Turc formula (or that of Hargreaves, etc.) offers a statistical estimation of PET. Ideally, these formulas should be recalibrated to regional scales. They are fairly well correlated with the PET Penman formula (in particular the Turc formula) but they underestimate the transpiration demand (particularly during the growing season) since neither the canopies albedo (influencing the radiative term) nor the wind speed or air humidity (there is no convective term) are taken into account.
- The Thornthwaite formula (or Blaney - Criddle, etc.) is relatively simple. As with Turc or Hargreaves, it offers a statistical estimation. Only the air temperature is taken into account. These PET formulas do not allow proper estimates of AET.
For forests, the Penman formula is considered the reference for calculating PET. It is easily adapts calculations for all geographic locations, all climates (historical data and future projections) and all cover types (deciduous / coniferous and varied LAI). All functions in the model Biljou© were calibrated using the Penman ETP. Use of formulas other than PET calculated by Biljou© would lead to biased results.
How are meteorological variables measured?
The table and the illustrations below show the different equipment that are commonly used to measure weather variables:

Probes for measuring temperature and air humidity
(left)
Automatic rain gauge
(right)

| variable | measuring device |
|---|---|
| global radiation | pyranometer |
| net radiation | pyrradiometer |
| temperature | thermometer, thermistor, thermocouple |
| air humidity | capacitive sensors |
| wind speed | anemometer (cups or sonic) |
| precipitation | rain gauge |
3D sonic anemometer

Pyranometer
(left)
Pyrradiometer
(right)

Useful reference
![]() Badeau V, Ulrich E (2008) RENECOFOR - Etude critique de faisabilité sur : la comparabilité des données météorologiques « RENECOFOR » avec
celles de Météo France, l’estimation de la réserve utile en eau du sol et le calcul des volumes d’eau drainée en vue du calcul de bilans
minéraux sur les placettes du sous-réseau CATAENAT. Editeur : Office National des Forêts, Direction Technique et Commercial Bois,
ISBN 978 – 2 – 84207 – 323 – 7, 108 p. et 166 pages annexes.
Badeau V, Ulrich E (2008) RENECOFOR - Etude critique de faisabilité sur : la comparabilité des données météorologiques « RENECOFOR » avec
celles de Météo France, l’estimation de la réserve utile en eau du sol et le calcul des volumes d’eau drainée en vue du calcul de bilans
minéraux sur les placettes du sous-réseau CATAENAT. Editeur : Office National des Forêts, Direction Technique et Commercial Bois,
ISBN 978 – 2 – 84207 – 323 – 7, 108 p. et 166 pages annexes.
![]() Peiffer M, Badeau V, Bréda N, Ulrich E (2008) RENECOFOR-Monitoring local forest weather conditions (France and Luxemburg)-report for
1995-2004. RENECOFOR-suivi de la météorologie forestière locale (France et Grand-Duché de Luxembourg). Bilan de la période 1995-2004.
Editeur : Office National des Forêts, Direction Technique et Commercial Bois, ISBN 978 – 2 – 84207 – 325 – 1, 313 p.
Peiffer M, Badeau V, Bréda N, Ulrich E (2008) RENECOFOR-Monitoring local forest weather conditions (France and Luxemburg)-report for
1995-2004. RENECOFOR-suivi de la météorologie forestière locale (France et Grand-Duché de Luxembourg). Bilan de la période 1995-2004.
Editeur : Office National des Forêts, Direction Technique et Commercial Bois, ISBN 978 – 2 – 84207 – 325 – 1, 313 p.
![]() Allen R G, Pereira L S, Raes D, Smith M ( 1998) Crop evapotranspiration - Guidelines for computing crop water requirements - FAO Irrigation
and drainage paper 56. Water Resources, Development and Management Service FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 1998.
Allen R G, Pereira L S, Raes D, Smith M ( 1998) Crop evapotranspiration - Guidelines for computing crop water requirements - FAO Irrigation
and drainage paper 56. Water Resources, Development and Management Service FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 1998.

